Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)
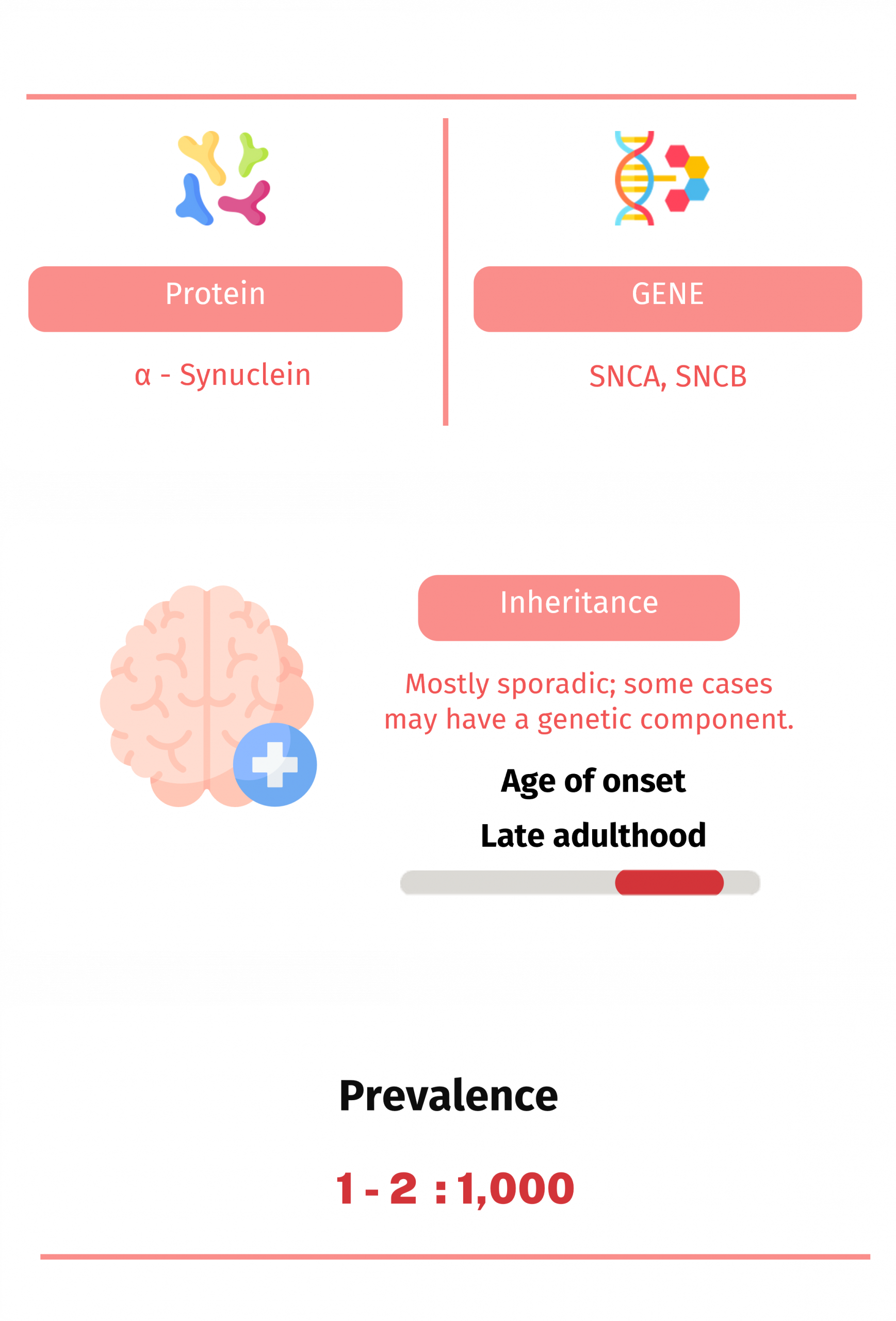
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a progressive brain disorder associated with the presence of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain. These deposits disrupt the normal functioning of brain cells and contribute to cognitive decline, visual hallucinations, movement difficulties, and fluctuations in alertness and attention. LBD shares similarities with both Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, making diagnosis and management complex.
The exact cause of LBD is not fully understood, but genetic and environmental factors may play a role. Management typically involves a multidisciplinary approach aimed at addressing cognitive, motor, and psychiatric symptoms, with the goal of improving quality of life for affected individuals and their caregivers.

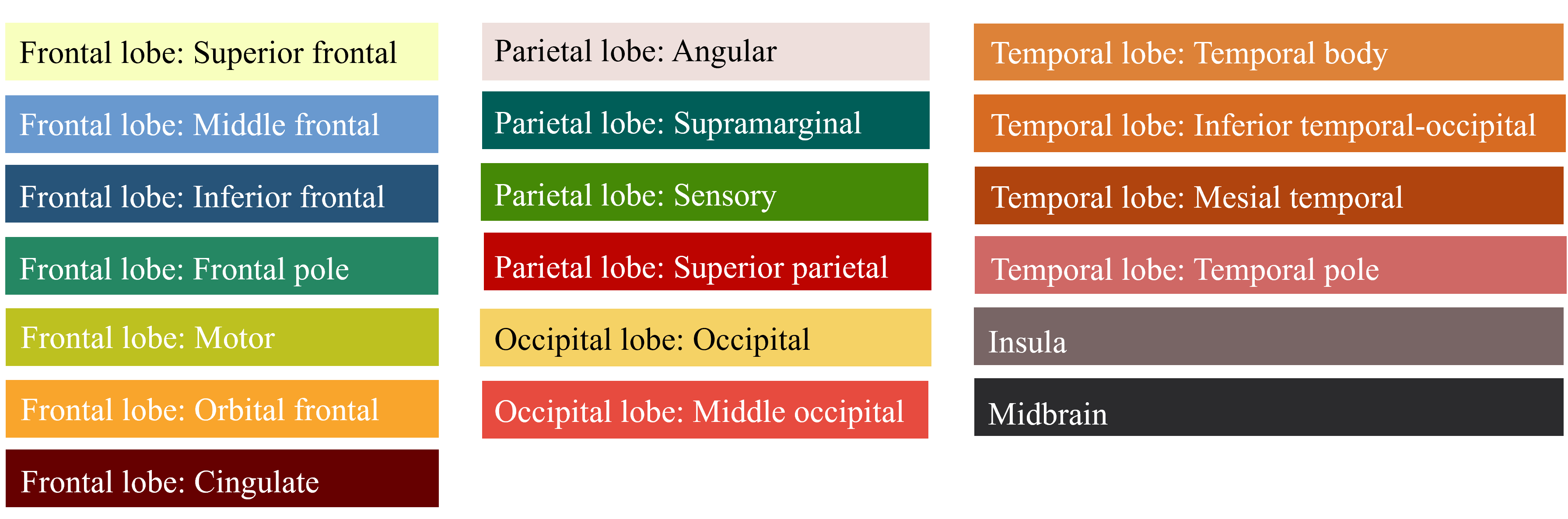
This figure shows the location of Lewy Body Dementia within the brain. Different colors represent various brain regions according to their labels, while the points indicate areas with a potential presence of Lewy Body Dementia.
Symptom
Symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) can vary among individuals but commonly include:
- Cognitive Decline: Memory loss, impaired executive function (planning, organizing, problem-solving), difficulty with attention and concentration.
- Visual Hallucinations: Seeing things that are not present, often vivid and detailed.
- Movement Difficulties: Bradykinesia (slowness of movement), rigidity (stiffness of muscles), tremor (especially at rest), gait changes such as shuffling or freezing.
- Fluctuations in Alertness and Attention: Episodes of confusion or disorientation, inconsistent levels of alertness throughout the day.
- REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: Acting out dreams during sleep, which may include talking, yelling, or physical movements.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure upon standing), urinary incontinence or retention, constipation.
- Behavioral and Psychiatric Symptoms: Depression, anxiety, agitation, delusions or paranoia.
- Sensitivity to Medications: Increased susceptibility to side effects from certain medications, especially antipsychotics.
- Speech and Swallowing Difficulties: Slurred speech, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), which may lead to choking or aspiration pneumonia.
- Sensitivity to Stimuli: Sensitivity to light, noise, or touch.
These symptoms can fluctuate in severity and may overlap with those of other neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Early recognition and management of symptoms are crucial for improving quality of life for individuals with LBD and their caregivers.