Krabbe Disease
Krabbe disease, also known as globoid cell leukodystrophy, is a rare lysosomal disorder that affects the white matter of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
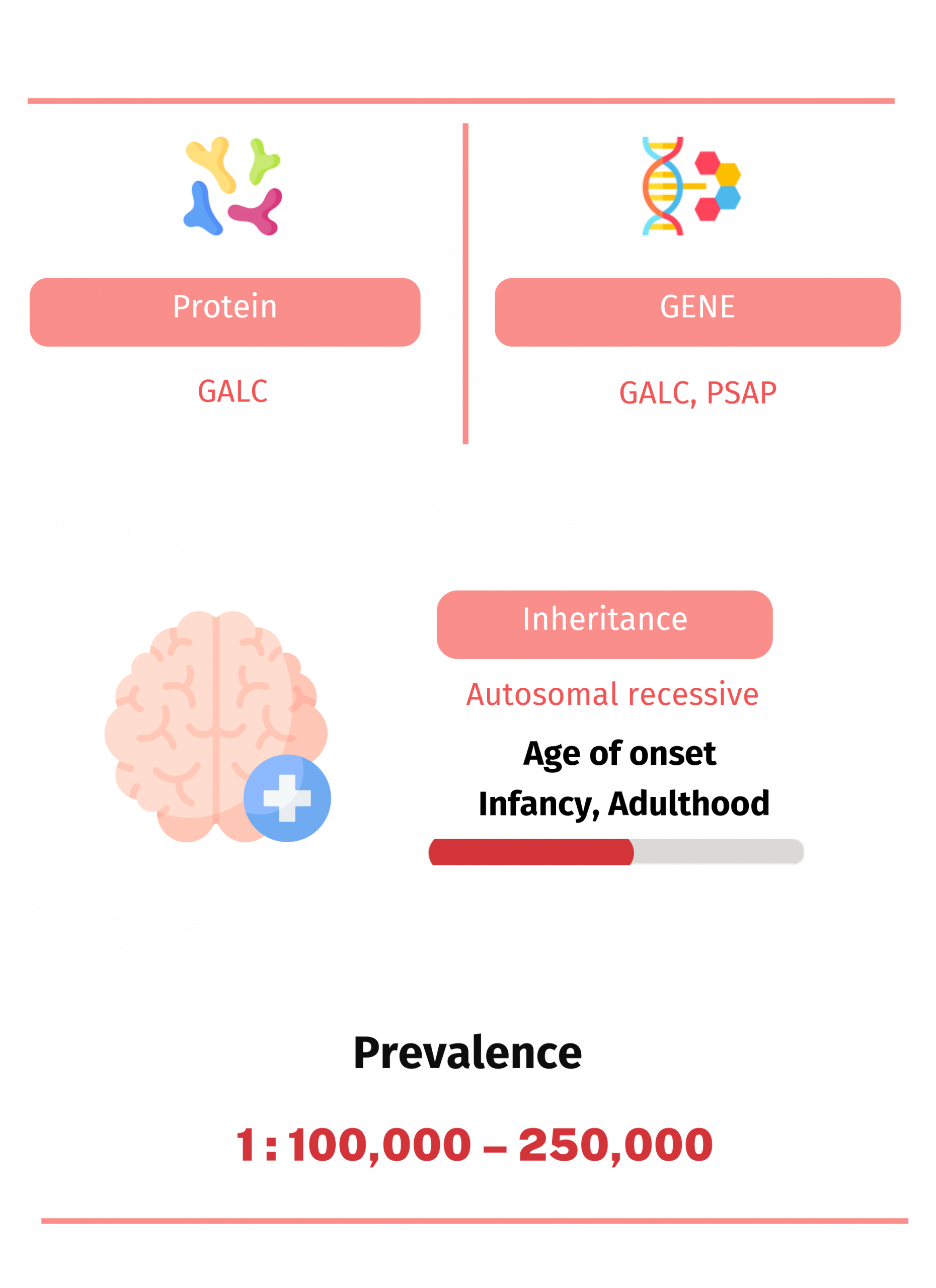
The disease is caused by mutations in the GALC gene, which encodes the lysosomal enzyme galactocerebrosidase (GALC). GALC is responsible for breaking down galactose from galactocerebroside and galactosylsphingosine (psychosine). The accumulation of cytotoxic psychosine leads to apoptosis of oligodendrocytes and demyelination of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
In rare cases, infantile Krabbe disease can be caused by mutations in the PSAP gene, which encodes prosaposin. Prosaposin is necessary for GALC activity.
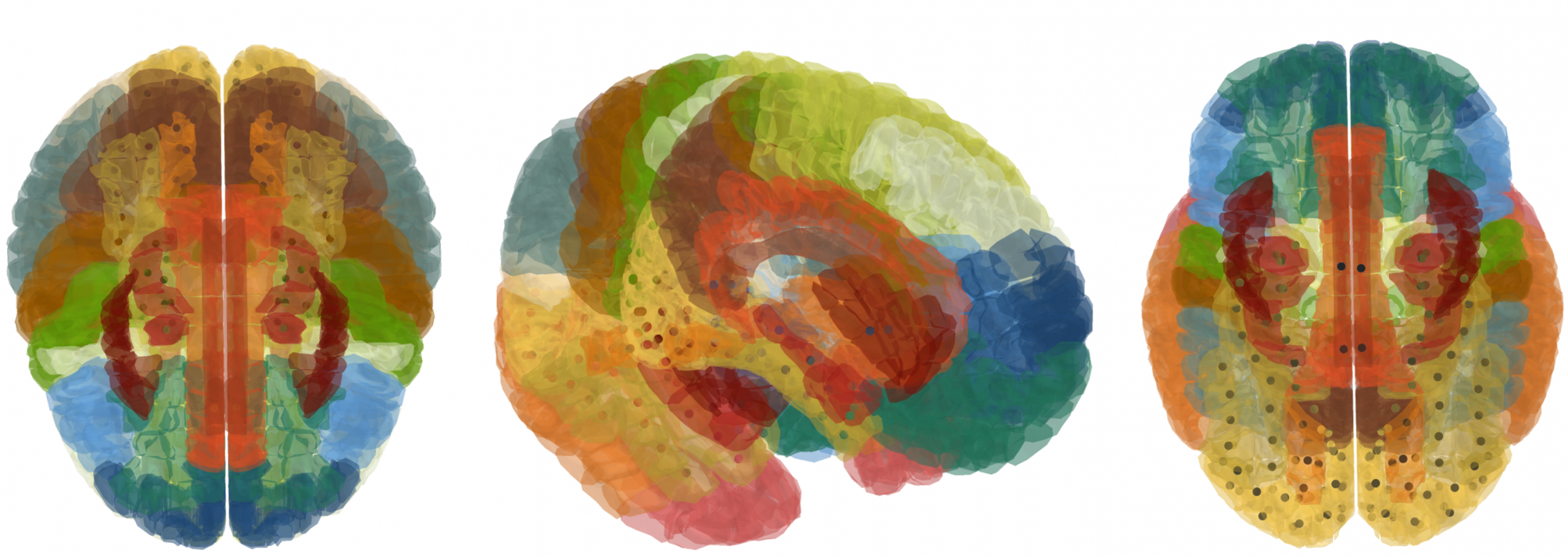
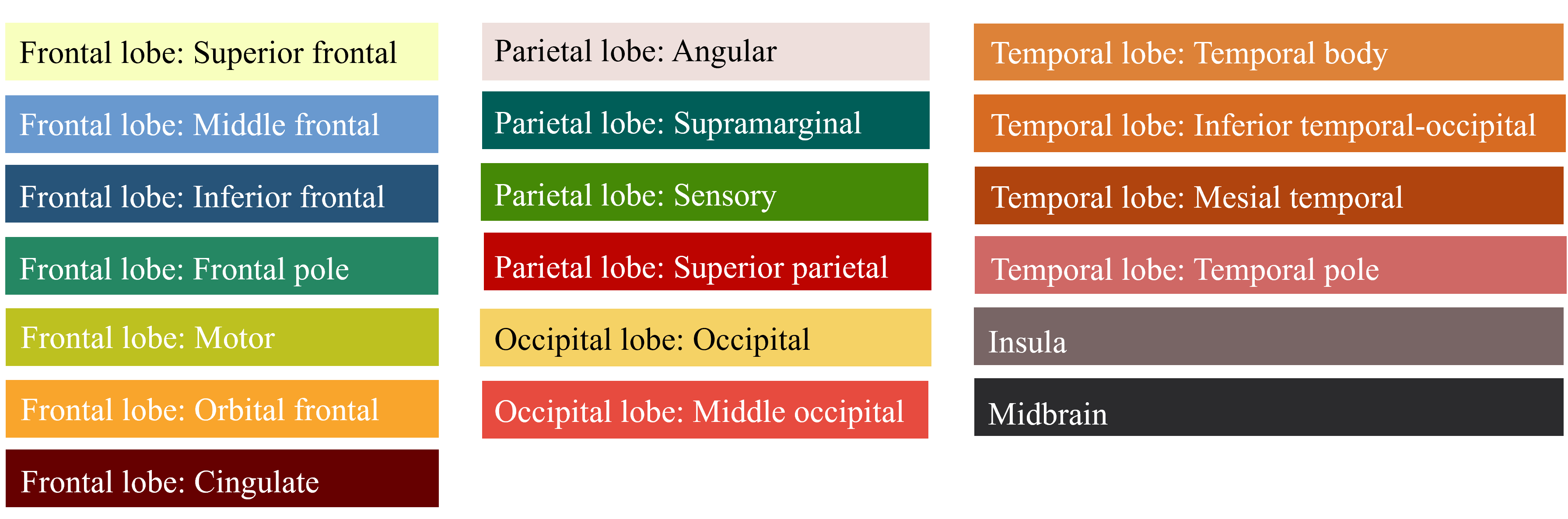
This figure shows the location of Krabbe Disease within the brain. Different colors represent various brain regions according to their labels, while the points indicate areas with a potential presence of Krabbe Disease.
Symptom
Symptoms of Krabbe disease may include:
- Developmental delay: Delay in achieving developmental milestones such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- Loss of motor skills: Progressive deterioration in motor function, leading to muscle weakness and difficulty with movement.
- Feeding difficulties: Challenges in feeding, swallowing, and gaining weight.Confusion
- Irritability: Excessive crying, fussiness, or irritability, which may be indicative of discomfort or pain.
- Seizures: Abnormal electrical activity in the brain resulting in seizures, which may manifest as convulsions or other seizure types.
- Muscle stiffness or rigidity: Increased muscle tone or stiffness, affecting mobility and flexibility.
- Vision and hearing impairments: Visual and auditory deficits, including vision loss, hearing loss, or other sensory impairments.
- Cognitive decline: Progressive deterioration in cognitive function, including memory loss, impaired judgment, and changes in behavior.
- Respiratory difficulties: Breathing problems, including shortness of breath, respiratory distress, or respiratory infections.
These symptoms can vary in severity and presentation among affected individuals, depending on the age of onset and the progression of the disease.