Huntington’s Disease (HD)
Huntington’s Disease (HD) is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system characterized by involuntary choreatic movements, behavioral and psychiatric disturbances, and dementia.
HD is caused by an elongated CAG repeat (36 repeats or more) in the huntingtin gene (HTT) located on the short arm of chromosome 4. The length of the CAG repeat is inversely correlated with the age of disease onset; the longer the repeat, the earlier the symptoms appear. This mutation leads to the production of an abnormal huntingtin protein, which accumulates in neurons, causing their dysfunction and death, particularly in the basal ganglia and cortex.
HD is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that each child of an affected parent has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation. There is currently no cure for HD, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
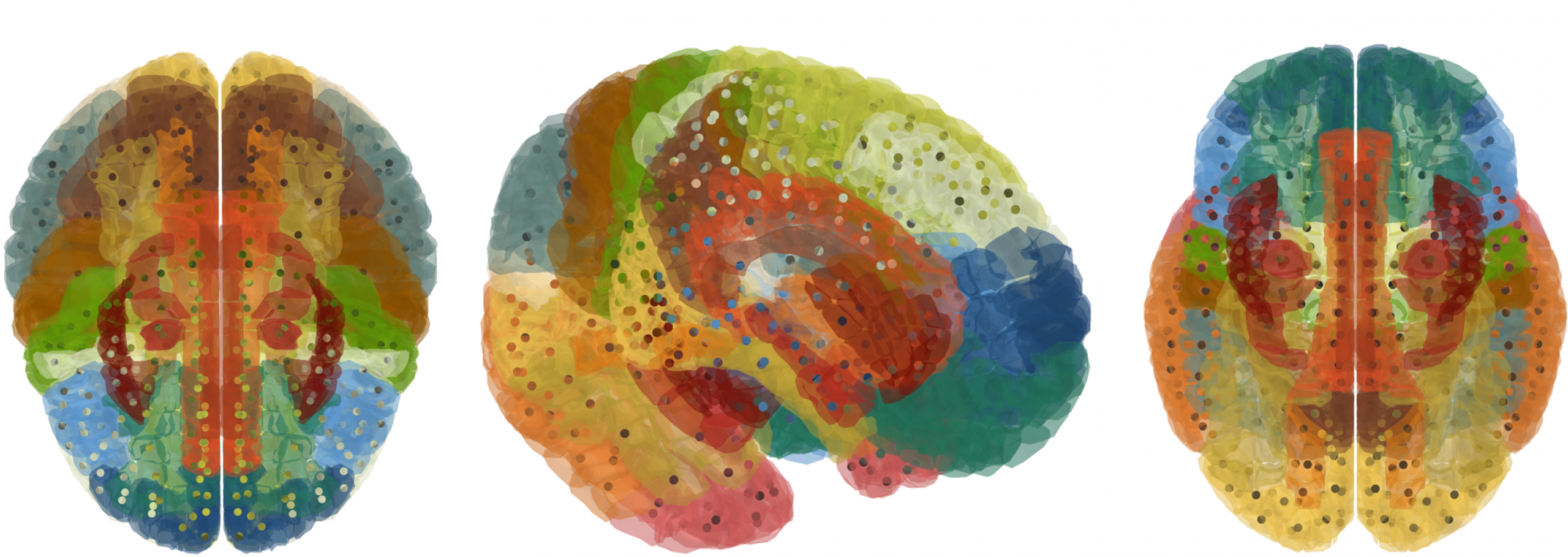
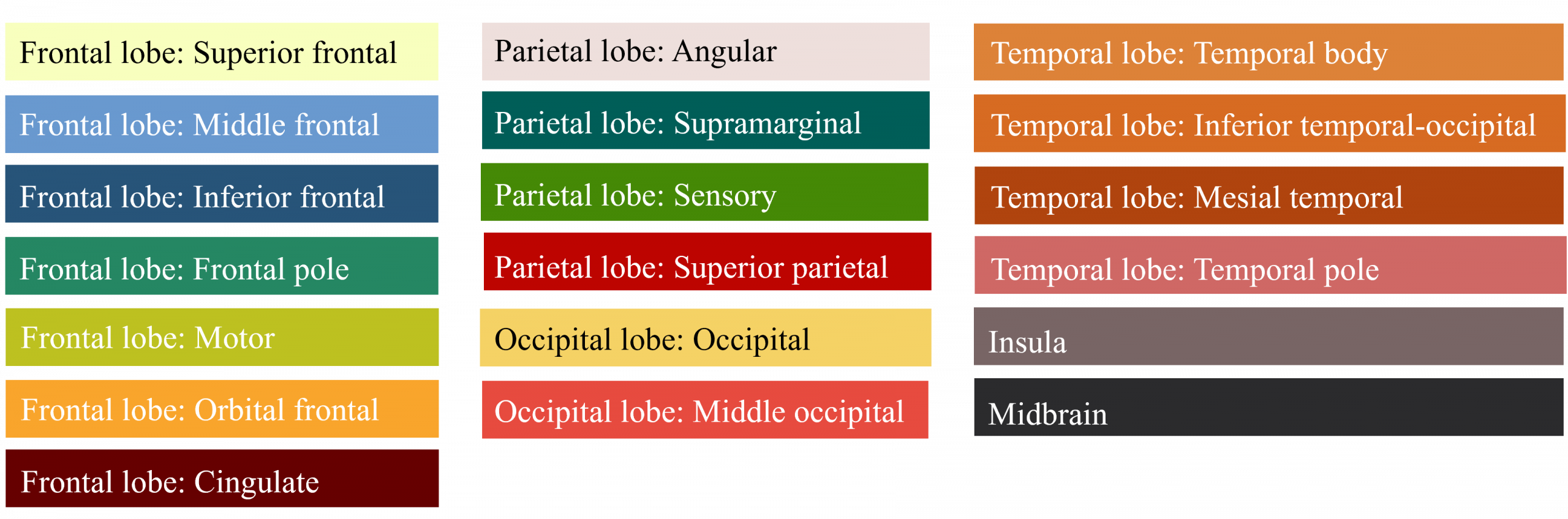
This figure shows the location of Huntington’s Disease within the brain. Different colors represent various brain regions according to their labels, while the points indicate areas with a potential presence of Huntington’s Disease.

Symptom
Symptoms of Huntington’s Disease (HD):
- Choreatic Movements: Involuntary, unpredictable movements of the face, limbs, and trunk.
- Coordination Problems: Difficulty with balance and fine motor tasks.
- Cognitive Decline: Problems with memory, concentration, and decision-making.
- Behavioral Changes: Irritability, anxiety, and depression.
- Psychiatric Disturbances: Mood swings, aggression, and obsessive-compulsive behaviors.
- Dementia: Progressive loss of cognitive function, affecting daily activities and independence.
- Speech Difficulties: Slurred speech and trouble articulating words.
- Swallowing Issues: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), leading to choking or aspiration.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss despite normal or increased appetite.
- Sleep Disturbances: Problems with sleeping patterns, such as insomnia or excessive daytime sleepiness.