Globular Glial Tauopathy (GGT)
Globular Glial Tauopathy (GGT) refers to a group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the abnormal accumulation of tau protein in brain cells, particularly astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. This accumulation results in the formation of globular inclusions, primarily in the white matter of the brain.
GGT encompasses a spectrum of disorders, including primary age-related tauopathy (PART) and other less common forms. Individuals with GGT typically experience cognitive impairment and various neurological symptoms. The exact cause of GGT is not fully understood, and there is currently no cure for this condition. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and providing supportive care to improve quality of life.

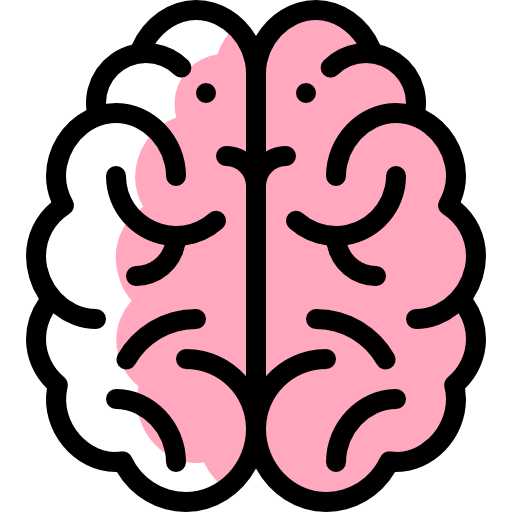
This figure shows the location of Globular Glial Tauopathy within the brain. Different colors represent various brain regions according to their labels, while the points indicate areas with a potential presence of Globular Glial Tauopathy.
Symptom
Symptoms of Globular Glial Tauopathy (GGT) can vary depending on the specific subtype and the areas of the brain affected. Common symptoms may include:
- Cognitive Impairment: Progressive decline in cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and executive function.
- Behavioral Changes: Alterations in behavior, mood swings, irritability, or apathy.
- Motor Dysfunction: Impairment in movement control, including stiffness, tremors, and difficulty with coordination.
- Speech and Language Difficulties: Problems with speaking (dysarthria) or understanding language.
- Visual Disturbances: Changes in vision, including blurry vision or difficulty with visual perception.
- Psychiatric Symptoms: Depression, anxiety, or other psychiatric disturbances.
- Functional Impairments: Difficulty with activities of daily living due to cognitive and motor deficits.
It’s important to note that the presentation of symptoms can vary among individuals and may depend on the specific subtype of GGT and the areas of the brain affected by tau protein accumulation.