Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)
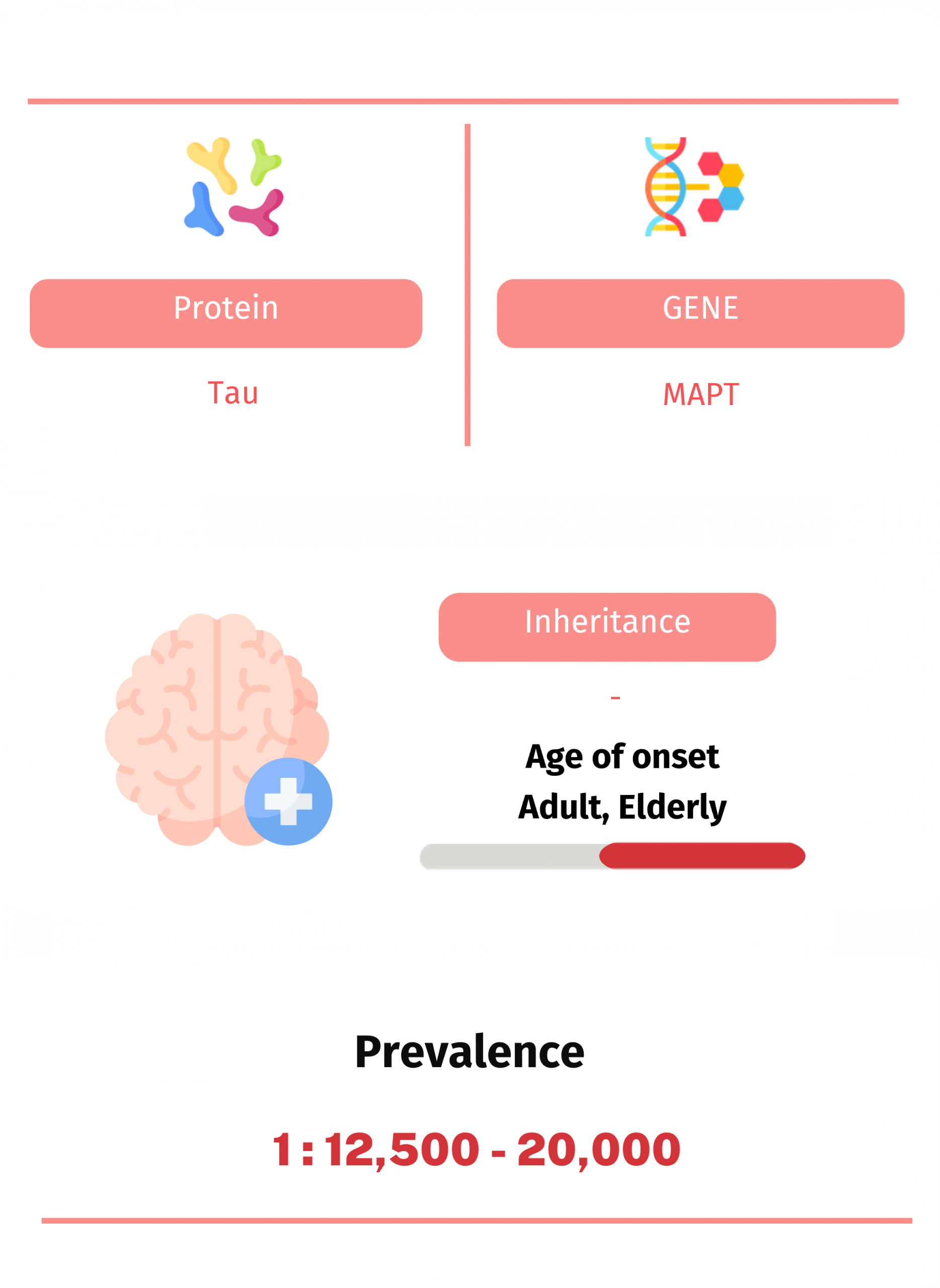
Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) is a rare neurologic disease characterized by multifaceted motor system dysfunctions and cognitive defects such as asymmetric rigidity, bradykinesia, limb apraxia, and visuospatial dysfunction. CBD is a distinct tauopathy with selective aggregation of 4 repeat tau proteins with characteristic antigenic and ultrastructural characteristics.
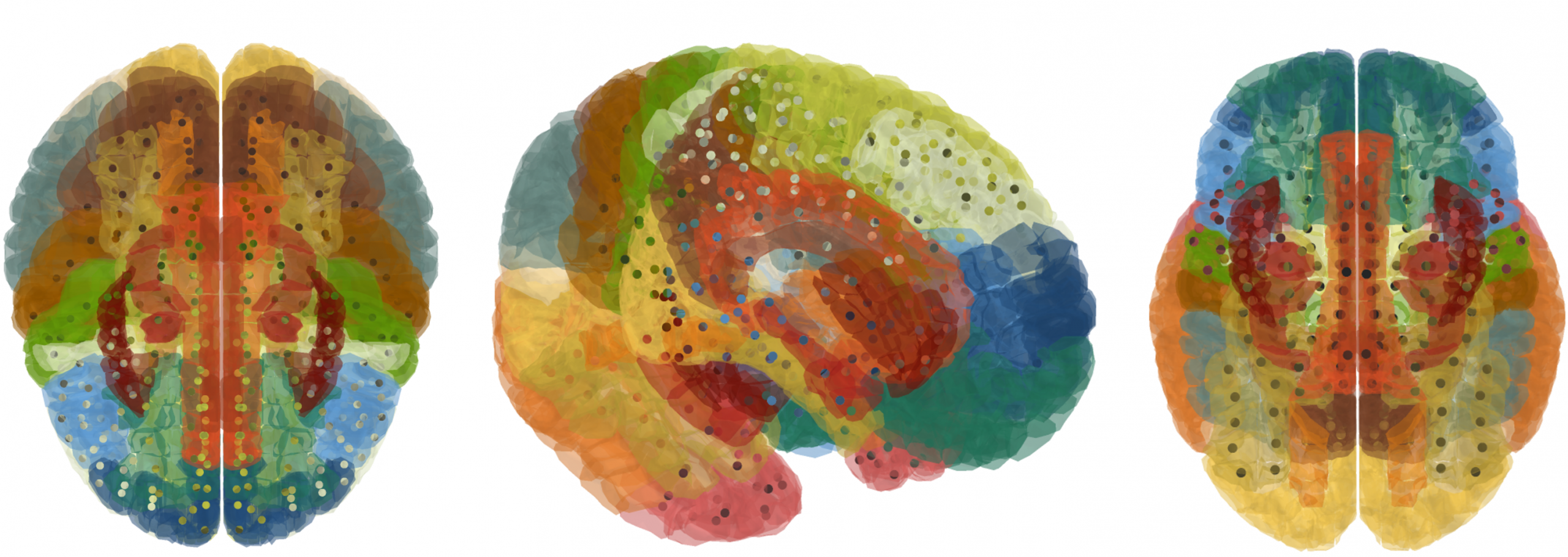
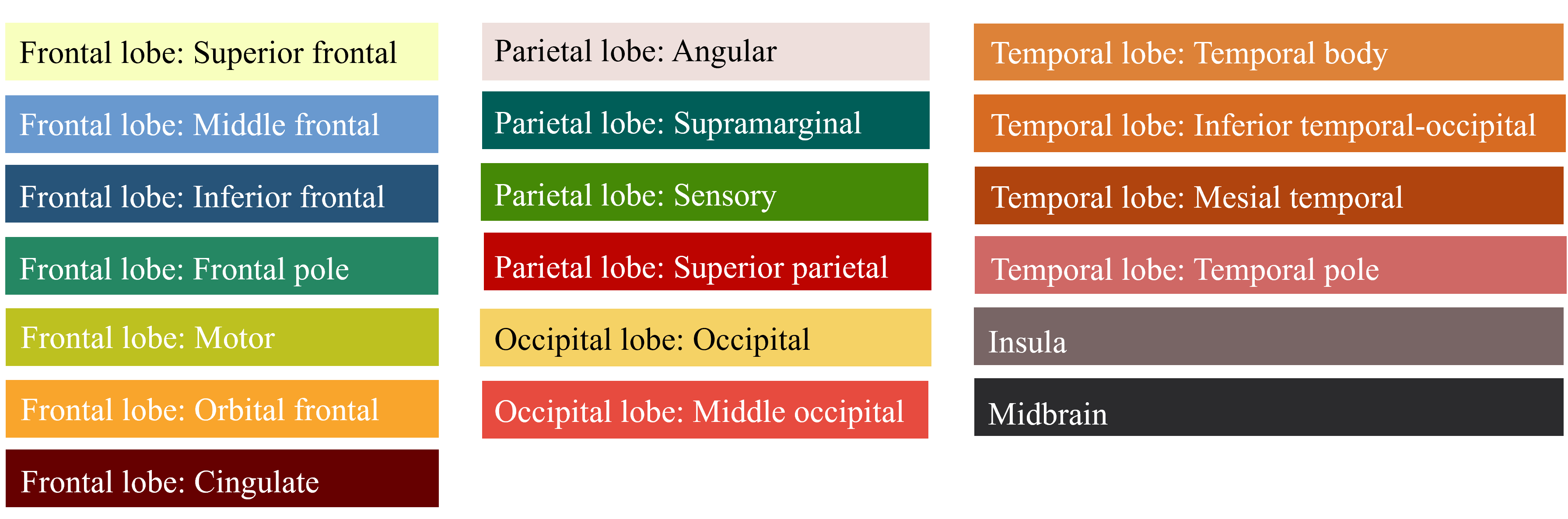
This figure shows the location of Corticobasal degeneration within the brain. Different colors represent various brain regions according to their labels, while the points indicate areas with a potential presence of Corticobasal degeneration.
Symptom
Symptoms of corticobasal degeneration (CBD) may include:
- Asymmetric Rigidity: Stiffness and resistance to movement, often affecting one side of the body more than the other.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, making everyday tasks more challenging.
- Limb Apraxia: Difficulty with purposeful movements, such as reaching or grasping objects, despite the absence of muscle weakness.
- Visuospatial Dysfunction: Impaired ability to perceive spatial relationships, leading to difficulties in navigating or judging distances.
- Cognitive Impairment: Decline in cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and executive function.
- Postural Instability: Difficulty maintaining balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls.
- Speech and Swallowing Difficulties: Dysarthria (difficulty speaking) and dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), which can impact communication and nutrition.
- Myoclonus: Involuntary muscle jerks or twitching, particularly affecting the limbs or face.
- Alien Limb Phenomenon: Sensation of the affected limb behaving involuntarily or as if it has a will of its own.
- Apathy and Behavioral Changes: Loss of interest in activities, emotional blunting, and alterations in mood or behavior.